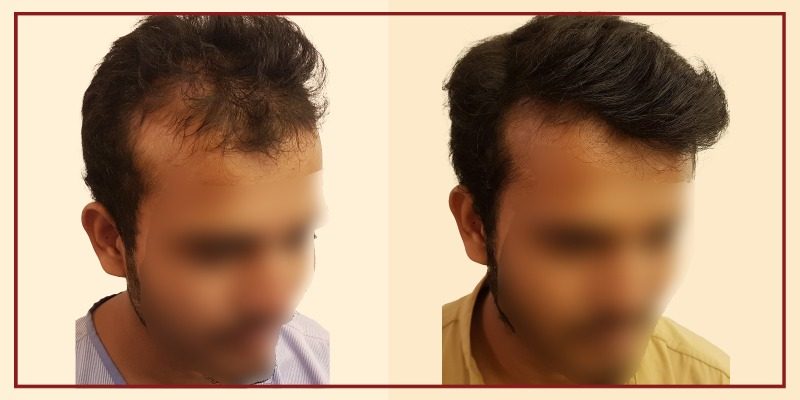
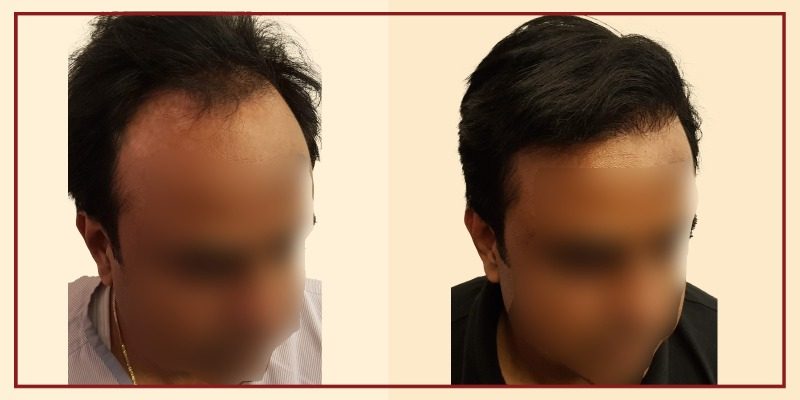
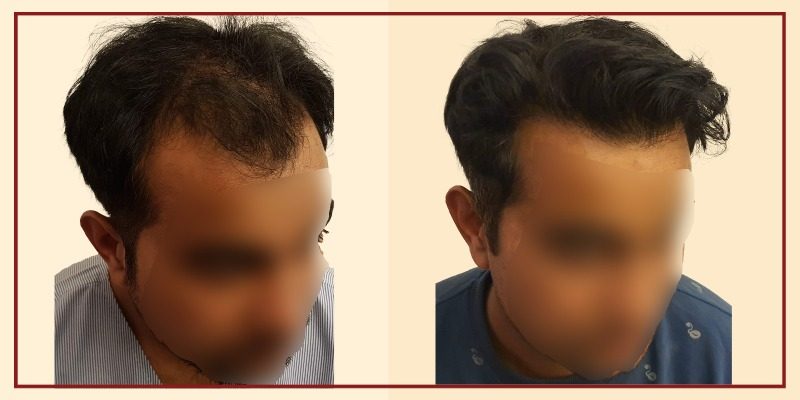
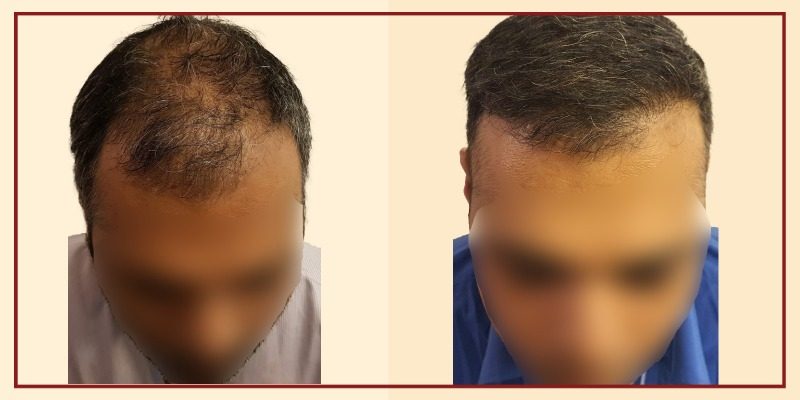
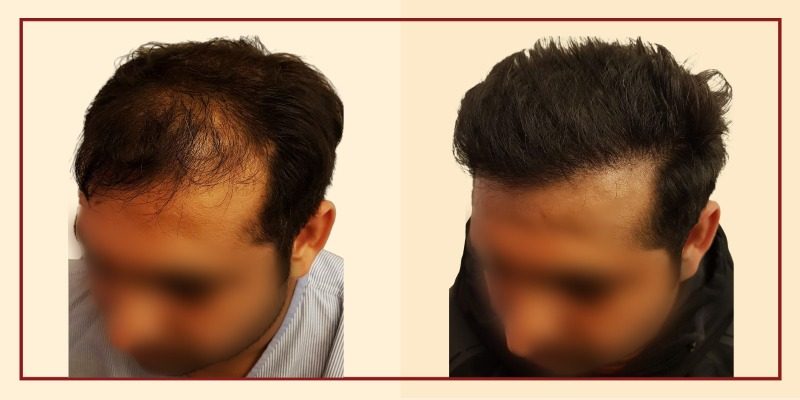
Hair Transplant In Men
Androgenetic alopecia or male pattern baldness is the most common cause of hair loss in men. A surgical hair transplant is the best solution to restore lost hair and for a long-lasting youthful appearance. In simple words, hair transplantation is a surgical technique where the surgeon transfers hair that the patient already has to an area with no hair. In medical terms, this technique makes use of hair grafts/hair follicles that are harvested from one part of the scalp/body where hair growth is comparatively denser, hormone-resistant and transplanted to a balding part of the scalp or any other body part. Hair grafts are one to three hair follicles harvested from a healthy part of the head (called the donor site), usually the back of the head, and transplanted to the bald area of the scalp, called as the recipient site. Hair transplants can also be used to restore beard, chest, eyelashes, eyebrows, and pubic hair.
Eligibility
It is very essential to check the eligibility criteria, to confirm if the patient is an ideal candidate to undergo Hair transplant surgery, to ensure a quick recovery and to achieve the desired results without any side effects. This makes it very important to consult a specialist or an expert surgeon with the required professional expertise and several years of experience in the field. Though any healthy male is eligible for the surgery, some factors make him an ideal candidate.
- Donor area – The donor area is usually the back part of the head from where hair follicles are extracted to be transplanted to the bald areas. If the quality and density of hair at the donor site are not high enough, their suitability may be questionable.
- The nature/type of hair loss– If the patient is suffering from conditions like alopecia areata hair transplantation surgery is not recommended unless there is no recurrence in the affected area for at least two year after completing non-surgical treatments. It is not an option for cases of Alopecia Totalis /Universalis but may be considered for localised cases of alopecia areata.
- Age – A healthy man who is over 20 – 25 years and suffers from male pattern baldness is eligible for a hair transplant.
- Nature of the scalp – A healthy looking scalp with no itching and inflammation are a pre requisite for the surgery. Acute inflammatory conditions of scalp are relative contraindications for surgery. We need to control the inflammation with medical treatments following which surgery can be considered.
- Diseases – Uncontrolled Hypothyroidism or Diabetes and patients with chronic diseases such as liver, kidney or heart failure cannot undergo a hair transplant. Diabetes, Cardiac and Thyroid cases under control are taken up for surgeries in consultation with their physician. Patients who have had chemotherapy for cancer shouldn’t consider a hair transplant as mostly this hair loss is reversible with medical therapies .
Importance Of Clinical Examination And Trichoscopy
An examination of the hair and scalp is a very important process to be undertaken before a patient undergoes hair transplant surgery. This includes an evaluation of hair density, nature of the scalp, the elasticity of the skin, view of the hair follicles, hair loss causes and pattern. These aspects have a long-lasting impact and important role to play in the procedure. A trichoscopic view of the hair follicles is an important factor in the success of a hair transplant surgery.
Trichoscopy can be used to assess the quality of potential donor hair sites prior to harvesting grafts. Hair density, follicular unit density, and hair shaft diameter are all critical factors in determining how much hair can be harvested from a given area. These parameters can also help determine the optimal location of the donor strip for FUT and FUE procedures. In general, the higher the number of FUs per square centimetre, the larger the donor strip that can be obtained.

Scalp Status
- Evaluating the nature of the scalp is crucial to choosing the best treatment protocol. Any signs of dryness like scales or flakes or signs of excess oil production like a shiny or muddy appearance are noted.
- The presence of any keratin residue or build-up in the hair follicle that may flake off like dandruff is also checked.
- The scalp is examined for any inflammation or sensitivity. If the capillaries are exposed, and the scalp is itchy or inflamed, that is to be addressed. The cause of inflammation should be investigated and treated.
Hair Density And Thickness
- The count of hair follicles in one centimetre of the scalp is counted to determine if it is average or below average.
- A strand of hair is measured for its diameter to determine if it is of normal thickness. Thinner hair below the threshold may indicate miniaturisation of the hair strand and, eventually, the hair follicle. In this case, it is important to intervene at an early stage with medical treatments and go ahead with the hair transplant after reversing the miniaturisation and stabilisation of the scalp.
Blood Work
Blood work is an essential part of the pre-hair transplant procedure- Random blood sugar, HIV tests, Hepatitis C and B tests, coagulation tests are mandatory. Blood tests to determine the cause of hair loss like serum iron/ ferritin profile, thyroid profile and hormone tests are also done. Other tests include the COVID- 19 RTPCR test, and ECG/EKG test in patients with cardiac complaints.
Importance Of Coagulation Tests
This test determines the time taken for blood to clot. This is very important for hair transplant since micro incisions are made on the scalp that causes bleeding. If the patient has a case of poor blood clotting, this may lead to serious problems like excessive bleeding.
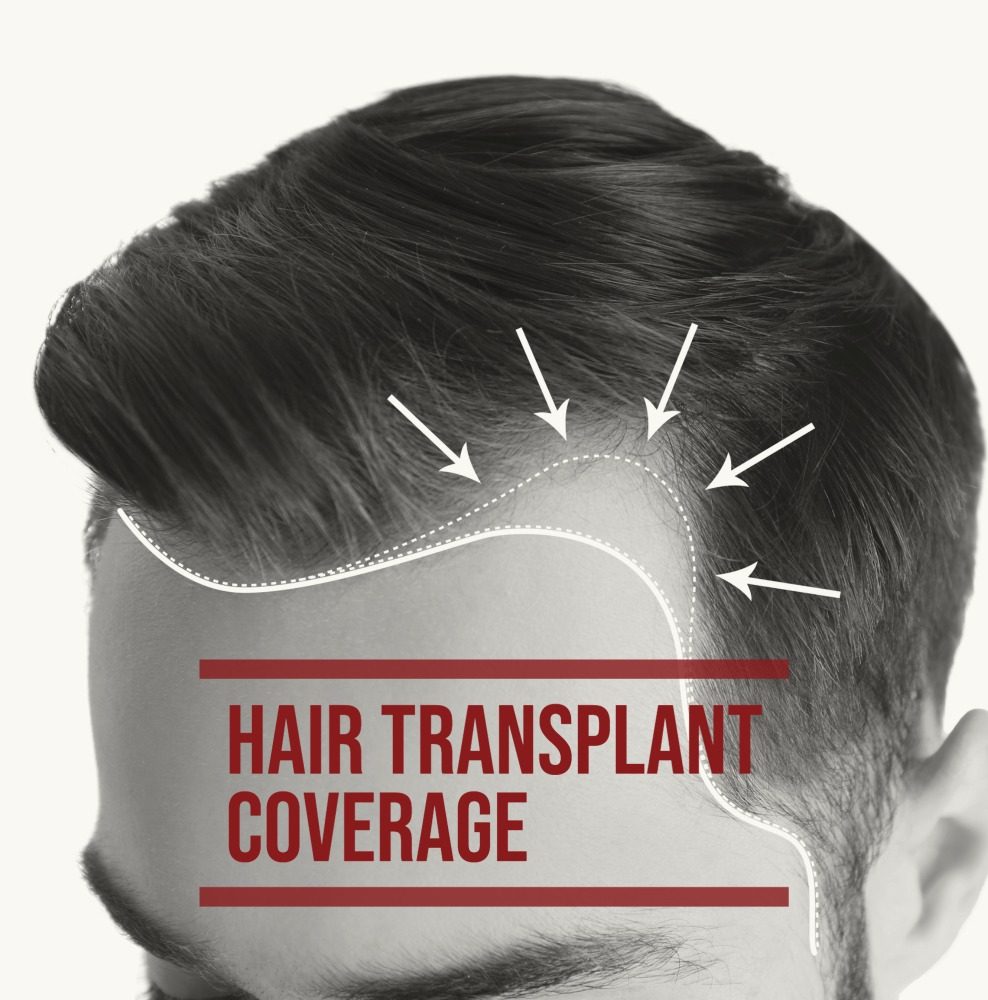
Planning Of Hair Transplant Coverage
One of the common questions posed to the surgeon by the patient is whether it is possible to achieve full coverage through hair transplant surgery. The answer to a full head hair transplant coverage depends on several factors ranging from the age of the patient, current balding pattern, availability of number of follicles in the donor area, the number of hair per follicular unit, any evidence of future hair loss and pattern of hair loss in the family etc. The answer to this also depends on each individual’s expectation of his hair restoration levels. This makes it a complex question that cannot have a simple yes or no answer.
In short, the number of hair graft estimates will determine the extent of hair restoration. It states how many grafts a patient may need to achieve different levels of coverage. As said before, the Norwood scale gives a reference for measuring the hair grafts (grafts/cm2) required by the balding area. On average it is estimated that a patient might need 1000 to 3000 hair grafts for coverage of half head of hair. Although each patient is different, it is estimated that an average of 6000 grafts are available in the donor site of the patient subject to the technique chosen .